A POST request in JavaScript is a way to send data to a server. It is one of the most common HTTP methods, and it is used for a variety of tasks, such as submitting forms, creating new resources, and updating existing resources.
POST requests are typically used when you need to send more data to the server than can be sent in a GET request. For example, if you are submitting a form with multiple fields, or if you are uploading a file, you will need to use a POST request.
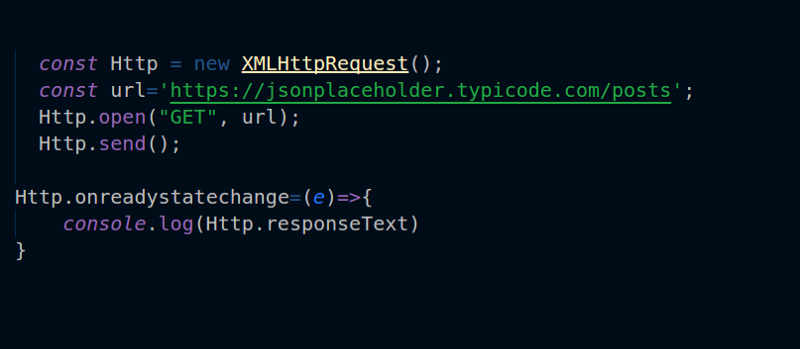
To send a POST request in JavaScript, you can use the XMLHttpRequest object. The XMLHttpRequest object is a built-in browser object that allows you to send and receive HTTP requests without reloading the page.
To send a POST request using the XMLHttpRequest object, you need to create a new XMLHttpRequest object and then call the open() method to specify the HTTP method and the URL of the resource you want to send the request to.
Once you have called the open() method, you need to set the request headers. The most important request header for POST requests is the Content-Type header. The Content-Type header tells the server what type of data you are sending in the request body.
For example, if you are sending JSON data in the request body, you would set the Content-Type header to application/json.
Once you have set the request headers, you can call the send() method to send the request. The send() method takes the request body as an argument.
The request body is the data that you want to send to the server. If you are sending JSON data, you would pass a JSON object to the send() method.
Once the request has been sent, you need to listen for the load event. The load event is fired when the response from the server has been received.
When the load event is fired, you can check the status property of the XMLHttpRequest object to see if the request was successful. If the status code is 200, then the request was successful.
If the request was successful, you can access the response data by calling the responseText property of the XMLHttpRequest object.
## Example of a POST Request in JavaScript
The following code shows an example of a POST request in JavaScript:
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); xhr.open("POST", "https://example.com/api/v1/users"); xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json"); const data = { name: "John Doe", email: "john.doe@example.com" }; xhr.send(JSON.stringify(data)); xhr.onload = function() { if (xhr.status === 200) { const user = JSON.parse(xhr.responseText); console.log(user); } else { console.log(xhr.statusText); } }; This code will send a POST request to the https://example.com/api/v1/users endpoint. The request body will contain a JSON object with the user's name and email address.
If the request is successful, the onload event handler will be called and the response data will be parsed into a JavaScript object. The user object can then be used in the application.
## When to Use POST Requests
POST requests should be used when you need to send data to a server that will cause a change to the state of the server. For example, if you are submitting a form to create a new user account, or if you are uploading a file to a server, you should use a POST request.
POST requests should also be used when you need to send more data to the server than can be sent in a GET request. For example, if you are submitting a form with multiple fields, or if you are uploading a large file, you should use a POST request.
## Benefits of Using POST Requests
POST requests have a number of benefits, including:
- Security: POST requests are more secure than GET requests because the data is sent in the request body. This means that the data is not visible in the URL, which makes it more difficult for attackers to intercept the data.
- Reliability: POST requests are more reliable than GET requests because they are not cached by the browser. This means that the data will always be sent to the server, even if the user has already visited the page.
- Flexibility: POST requests can be used to send any type of data to the server. This makes them more flexible than GET requests, which are typically used to
WebIn web development, a postback is an HTTP POST to the same page that the form is on. In other words, the contents of the form are POST ed back to the same URL as the form. [1]. WebPost/Redirect/Get ( PRG) is a web development design pattern that lets the page shown after a form submission be reloaded, shared, or bookmarked without ill effects, such as. WebCross-site scripting(XSS) is a type of security vulnerabilitythat can be found in some web applications. XSS attacks enable attackers to injectclient-side scriptsinto web pages. WebWeb pages may be redirected to a new domain for three reasons: a site might desire, or need, to change its domain name; an author might move their individual pages to a new. WebIf data is sent in any other format (JSON, XML) a standard method is to issue a POST request using XMLHttpRequest with CSRF attacks prevented by Same-origin policy. WebJSONP, or JSON-P (JSON with Padding), is a historical JavaScript technique for requesting data by loading a <script> element, [1] which is an element intended to load.
How To Make a POST Request With JavaScript

Source: Youtube.com
GET And POST Method In Express JS | Handling HTTP GET And POST Request With Express JS | Simplilearn

Source: Youtube.com
What Is A Post Request Javascript, How To Make a POST Request With JavaScript, 3.64 MB, 02:39, 47,792, codebubb, 2019-09-10T18:00:10.000000Z, 2, Here are the most popular ways to make an HTTP request in JavaScript, 349 x 800, jpg, , 3, what-is-a-post-request-javascript
What Is A Post Request Javascript.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to make a POST request with JavaScript. Get my free 32 page eBook of JavaScript HowTos 👉 bit.ly/2ThXPL3
Here's a link to the POST server I used in the tutorial: gist.github.com/codebubb/0c32460d67ee99dec8a455b59ef82c57
So there are no built in features with JavaScript to make network requests however there are plenty of tools available to actually send GET and POST requests.
You could use a library like jQuery, a purpose module like Axios but in the tutorial we'll use the fetch API to send our POST request.
I'll start off by showing you how to send a GET request with fetch, then i'll show you how to configure fetch with options to modify the type of request to POST and also send some data to a back end script. Channel Handle @codebubb
What Is A Post Request Javascript, WebWeb pages may be redirected to a new domain for three reasons: a site might desire, or need, to change its domain name; an author might move their individual pages to a new. WebIf data is sent in any other format (JSON, XML) a standard method is to issue a POST request using XMLHttpRequest with CSRF attacks prevented by Same-origin policy. WebJSONP, or JSON-P (JSON with Padding), is a historical JavaScript technique for requesting data by loading a <script> element, [1] which is an element intended to load.

Here are the most popular ways to make an HTTP request in JavaScript - Source: freecodecamp.org

node.js - How to send javascript date object with POST request in REST CLIENT (vs code extension)? - Stack Overflow - Source: stackoverflow.com
"Sorry, we just updated this page" error using HTTP POST Request - Source: community.dynamics.com
dev.to › davidking › a-guide-to-http-post-requestsA Guide To HTTP POST Requests In JavaScript - DEV Community
In conclusion, sending an HTTP POST request in JavaScript can be easily achieved using the fetch API. The fetch API provides a simple and convenient way to make network requests and handle responses. To send a POST request, you can specify the desired endpoint URL, the request method as POST, the body of the request, and the request headers. .
www.freecodecamp.org › news › javascript-postJavaScript POST Request – How to Send an HTTP POST Request in JS
With jQuery, you can access the POST method $.post(), which takes in three parameters: the API endpoint/URL, the data to be sent to the server, and a callback function that runs when the request is successful. const body = { userId: 1, title: "Fix my bugs", completed: false }; Post request example.
Post request example
Post request example What is difference between get request and post request.
.
What is difference between get request and post request
What is difference between get request and post request What is a post request javascript.
.
What is a post request javascript
What is a post request javascript What is difference between get request and post request.
.
zetcode.com › javascript › get-post-requestJavaScript get/post request - how to send HTTP GET and POST ...
In such a case, the default request is the GET request. let text = await res.text(); We get the body from the request as plain text. JS fetch POST request. In the next example we create a POST request with JSON data. .
.
.
.
.
.
.
www.geeksforgeeks.org › difference-between-get-andDifference between GET and POST request in Vanilla JavaScript
Javascript. Difference between GET and POST: 1. GET retrieves a representation of the specified resource. POST is for writing data, to be processed to the identified resource. 2. It typically has relevant information in the URL of the request. It typically has relevant information in the body of the request. 3. .
kinsta.com › knowledgebase › javascript-http-requestA Guide to JavaScript HTTP Requests - Kinsta
XMLHttpRequest is a built-in JavaScript object used for interacting with servers and loading content in web pages without reloading the browser. In this section, you'll see how to send POST, GET, PUT/PATCH, and DELETE requests using XMLHttpRequest. AJAX is used to make asynchronous HTTP requests. .
stackoverflow.com › questions › 6396101Pure JavaScript Send POST Data Without a Form - Stack Overflow
13. There is an easy method to wrap your data and send it to server as if you were sending an HTML form using POST . you can do that using FormData object as following: data = new FormData() data.set('Foo',1) data.set('Bar','boo') let request = new XMLHttpRequest(); request.open("POST", 'some_url/', true); .
developer.mozilla.org › docs › WebPOST - HTTP | MDN - MDN Web Docs
The HTTP POST method sends data to the server. The type of the body of the request is indicated by the Content-Type header.. The difference between PUT and POST is that PUT is idempotent: calling it once or several times successively has the same effect (that is no side effect), where successive identical POST may have additional effects, like passing an order several times. .
Post a Comment