
LoRA stands for Low-Rank Adaptation. It is a technique for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) and other deep learning models in a parameter-efficient way. LoRA works by learning a low-rank matrix that is used to adapt the weights of the pre-trained model to the new task. This approach has several advantages over traditional fine-tuning methods, including:
- Reduced memory and compute requirements: LoRA requires significantly fewer trainable parameters than traditional fine-tuning methods, which can lead to significant savings in memory and compute resources.
- Faster convergence: LoRA models typically converge faster than traditional fine-tuning models, especially on small datasets.
- Improved performance: LoRA models have been shown to achieve better performance than traditional fine-tuning models on a variety of tasks, including question answering, summarization, and translation.
LoRA is a relatively new technique, but it has quickly gained popularity in the machine learning community. It is currently being used to fine-tune LLMs such as Bard, GPT-3, and LaMDA for a variety of tasks, including:
- Generating different creative text formats: LoRA can be used to fine-tune LLMs to generate different creative text formats, such as poems, code, scripts, musical pieces, email, letters, etc.
- Translating languages: LoRA can be used to fine-tune LLMs to translate languages more accurately and fluently.
- Answering questions in a comprehensive and informative way: LoRA can be used to fine-tune LLMs to answer questions in a more comprehensive and informative way, even if they are open ended, challenging, or strange.
How LoRA works
LoRA works by learning a low-rank matrix that is used to adapt the weights of the pre-trained model to the new task. This low-rank matrix is typically much smaller than the original weight matrix, which leads to significant savings in memory and compute resources.
To fine-tune a model with LoRA, we first need to define a set of adaptation parameters. These adaptation parameters are used to control how much the weights of the pre-trained model are adapted to the new task.
Once we have defined the adaptation parameters, we can train the LoRA model by minimizing the following loss function:
loss = L(f(x; W + U * A), y) where:
fis the pre-trained modelWis the original weight matrix of the pre-trained modelUis the low-rank adaptation matrixAis the adaptation parametersLis a loss function, such as cross-entropy or mean squared errorxis the input datayis the target output
The goal of training is to find the values of U and A that minimize the loss function. This can be done using a variety of optimization algorithms, such as gradient descent.
Once the LoRA model is trained, it can be used to make predictions on new data by simply passing the input data through the model:
y_hat = f(x; W + U * A) The output of the model will be the predicted output for the given input data.
Benefits of using LoRA
There are several benefits to using LoRA to fine-tune large language models and other deep learning models:
- Reduced memory and compute requirements: LoRA requires significantly fewer trainable parameters than traditional fine-tuning methods, which can lead to significant savings in memory and compute resources. This is especially important for training and deploying large language models, which can have billions of parameters.
- Faster convergence: LoRA models typically converge faster than traditional fine-tuning models, especially on small datasets. This is because LoRA adapts the weights of the pre-trained model in a more targeted way.
- Improved performance: LoRA models have been shown to achieve better performance than traditional fine-tuning models on a variety of tasks, including question answering, summarization, and translation. This is because LoRA adapts the weights of the pre-trained model in a way that is better suited to the specific task.
Example of using LoRA
To illustrate how to use LoRA, let's consider the following example:
We want to fine-tune a large language model to translate
WebLoRa — The Low-Rank Adaptation Everyone Talks About. LoRa, or Low-Rank Adaptation, is a fine-tuning technique that can adapt large language models. WebTorch Concepts. LoRA (Low Rank Adaptation) is a new technique for fine-tuning deep learning models that works by reducing the number of trainable parameters. WebThere are several directories in this repo: loralib/ contains the source code for the package loralib, which needs to be installed to run the examples we provide; examples/NLG/.
LoRA - Low-rank Adaption of AI Large Language Models: LoRA and QLoRA Explained Simply

Source: Youtube.com
Intro to LoRA Models: What, Where, and How with Stable Diffusion

Source: Youtube.com
What Is Ai Lora, LoRA - Low-rank Adaption of AI Large Language Models: LoRA and QLoRA Explained Simply, 6.36 MB, 04:38, 10,306, Wes Roth, 2023-06-01T23:49:15.000000Z, 2, Stable Diffusion: What Are LoRA Models and How to Use Them?, 470 x 1000, jpg, , 3, what-is-ai-lora
What Is Ai Lora. WebWe propose Low-Rank Adaptation, or LoRA, which freezes the pre-trained model weights and injects trainable rank decomposition matrices into each layer of the.
What is LoRA in AI?
You may have heard of a concept called LoRA or QLoRA referring to AI and Large Language Models.
Imagine you have a giant box full of Legos.
You can build all kinds of things with this giant box - houses, cars, spaceships.
But it's so big and heavy that it's hard to carry around.
And most of the time, you don't need all these Legos to build what you want to build.
So instead, you pick out a smaller box of your favorite, most useful Legos.
This smaller box is easier to carry around, and you can still build most of the things you want.
In this analogy, the giant box of Legos is like a large language model, like GPT-4.
It's powerful and can do lots of things, but it's also big and heavy (it requires a lot of computational resources to use).
The smaller box of Legos is like a "low-rank adaptation" of the large language model.
It's a smaller, lighter version of the model that's been adapted for a specific task.
It's not as powerful as the full model - there might be some things it can't do - but it's more efficient and easier to use.
"Low-Rank Adaptation"
LoRA stands for
"Low-Rank Adaptation"
"Low-rank" in this context refers to a mathematical technique used to create this smaller, lighter model.
You can also think of "Low-Rank" as just reading all the highlighted parts in a book.
"Full Rank" would be reading the entire book and "Low-Rank" would be reading just the important, highlighted parts.
Why is LoRA important?
Let's say you have a large and advanced AI model trained on recognizing all sorts of images.
You can "fine-tune" it to do a related task (like recognizing images of cats, specifically) by making small adjustments to that large model.
You can also "fine-tune" it to add behaviors you want or remove behaviors you don't.
But this can be very expensive in terms of what computers you would need and how long it would take.
Lora solves this problem by making it cheap and fast to fine tune smaller models
LoRA is important because:
1. Efficiency
Using LoRA can greatly reduce the amount of resources used to train AI models to perform these tasks.
2. Speed
These lower-rank models are faster to train,but they also can provide faster outputs.
This can be crucial in applications where results need to happen in real-time.
3. Limited Resources
In many real world applications the devices that are available to run AI models may have limited computational power or memory.
Your smartphone may not be able to run a large AI model, but a Low-Rank Adaptation can be used for specific tasks you may need.
4. Stacking and Transfering
Low-rank adaptations can be helpful for transfer learning where a model trained on one task can be adapted to a different, but related task.
This is much more efficient than training the large model to do something from scratch.
The updates and new skills learned by these low rank adaptations can also stack with other such adaptations, so multiple models can benefit each other as well as the original larger model.
QLoRa
QLoRA is a similar concept.
The Q is for Quantized, so QLoRA is Quantized Low Rank Adaptation.
Quantized refers to data compression.
Quantization is converting a continuous range of values into a finite set of possible values.
Image if you're an artist mixing paint.
You have an almost infinite range of colors you can create by mixing different amounts of colors together.
This is like a continuous signal in the real world.
But if you are working with a computer graphics program, it can't handle an infinite range of colors.
It might only allow each color component (red, green, and blue) to have one of several levels of intensity.
This limited set of possible colors is like a quantized signal.
Here it can apply to reducing the number of decimal places we need to express a number.
For example Pi is an infinitely long number, but we can use 3.14 as an approximation when doing calculations.
Hope you liked that!
Take a look at our next video or checkout our top watched videos in the descriptions
What Is Ai Lora, WebTorch Concepts. LoRA (Low Rank Adaptation) is a new technique for fine-tuning deep learning models that works by reducing the number of trainable parameters. WebThere are several directories in this repo: loralib/ contains the source code for the package loralib, which needs to be installed to run the examples we provide; examples/NLG/.

Stable Diffusion: What Are LoRA Models and How to Use Them? - Source: softwarekeep.com

Hugging Face's LoRA is a Simple Framework for Fine-Tuning Text-to-Image Models | by Jesus Rodriguez | Towards AI - Source: pub.towardsai.net
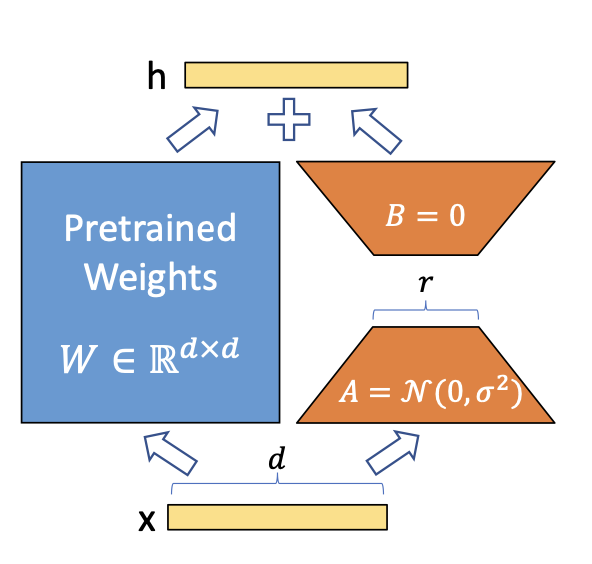
Posit AI Blog: Understanding LoRA with a minimal example - Source: blogs.rstudio.com
What is lora in generative ai
What is lora in generative ai What is lora in ai image generation.
What is lora in ai image generation
What is lora in ai image generation What is lora ai reddit.
What is lora ai reddit
What is lora ai reddit What is lora ai art.
.
What is lora ai art
What is lora ai art What is ai lora.
.
What is ai lora
What is ai lora What is lora ai art.
medium.com › rendernet › demystifying-loras-what-areDemystifying LoRAs: What are they and how are they used in ...
As their name implies, LoRAs are a class of mathematical operations crucial to neural networks. These operations are fundamental components of generative models, such as Generative Adversarial, What is sir lora.
github.com › microsoft › LoRALoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models
LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. This repo contains the source code of the Python package loralib and several examples of how to integrate it with PyTorch models, such as those in Hugging Face. We only support PyTorch for now. See our paper for a detailed description of LoRA. LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models. .
.
.
.
www.generativelabs.co › post › lora-models-aGetting Familiar with LoRA Models: A Beginner's Guide
LoRA stands for Low-Rank Adaptation, a cool technology that makes it easier to train Stable Diffusion on different concepts, such as characters or styles. In simpler terms, it lets you fine-tune your AI-generated art, making it more vibrant and alive. .
toloka.ai › blog › lora-modelsLoRA AI models: Low-Rank Adaptation for a More Efficient Fine ...
LoRA or Low Rank Adaptation is an approach that presents parameter efficient fine tuning for Large Language Models. However, it was only in the early days of LoRA existence that this technique could be applied only to LLMs. Now LoRA training is applied, for example, for image-generating models like Stable Diffusion models as well. .
.
What is sir lora
What is sir lora What does sir lora do.
What does sir lora do huggingface.co › blog › loraUsing LoRA for Efficient Stable Diffusion Fine-Tuning
What does sir lora do What is lora.
What is lora www.entrypointai.com › blog › lora-fine-tuningLoRA Fine-tuning & Hyperparameters Explained (in Plain ...
What is lora November 24th, 2023. Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) method is a fine-tuning method introduced by a team of Microsoft researchers in 2021. Since then, it has become a very popular approach to fine-tuning large language models, diffusion models (such as for image-generation), and other types of AI models. How does lora work.
How does lora work softwarekeep.com › blogs › how-toStable Diffusion: What Are LoRA Models and How to Use Them?
How does lora work LoRA stands for Low-Rank Adaptation. It allows you to use low-rank adaptation technology to quickly fine-tune diffusion models. To put it in simple terms, the LoRA training model makes it easier to train Stable Diffusion on different concepts, such as characters or a specific style. What is lora in generative ai.
Post a Comment