
HTTP is the Hypertext Transfer Protocol, and it is the foundation of the World Wide Web. It is used to transfer data between clients and servers, and it is the protocol that allows you to view web pages in your browser.
An HTTP request is a message that a client sends to a server. It contains information about the resource that the client wants to access, as well as the desired action that the server should take.
The most common HTTP request method is GET. This method is used to retrieve a resource from the server. For example, when you visit a web page in your browser, you are sending a GET request to the server for the HTML file that makes up the web page.
Other HTTP request methods include:
- POST: This method is used to create or update a resource on the server. For example, when you submit a form on a web page, you are sending a POST request to the server with the data from the form.
- PUT: This method is used to replace an existing resource on the server with a new one. For example, when you upload a file to a web server, you are sending a PUT request to the server with the file data.
- DELETE: This method is used to delete a resource from the server. For example, when you delete a file from a web server, you are sending a DELETE request to the server.
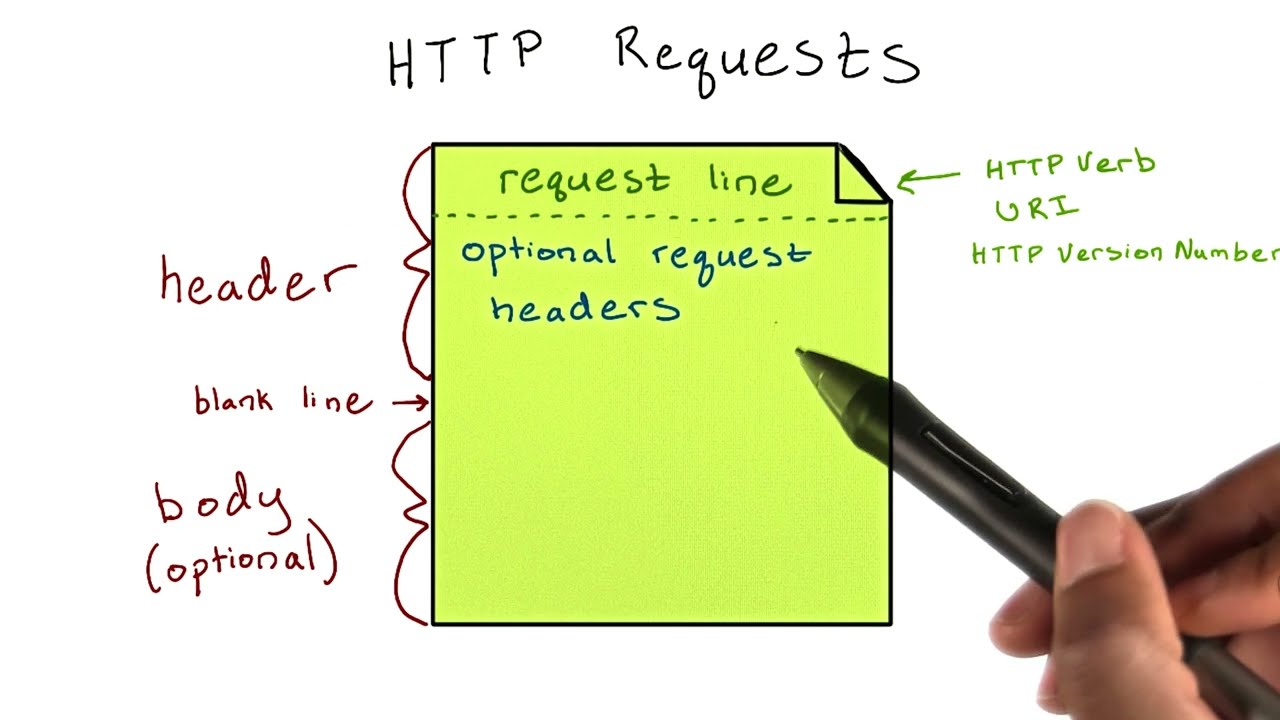
Anatomy of an HTTP Request
An HTTP request consists of three parts:
- Request line: The request line contains the HTTP method, the resource path, and the HTTP version.
- Request headers: The request headers contain additional information about the request, such as the content type of the request body and the client's Accept header, which specifies the types of responses that the client is willing to accept.
- Request body: The request body is optional, and it contains the data that the client is sending to the server.
For example, the following is an HTTP GET request for the web page https://example.com/index.html:
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1 Host: example.com This request line specifies that the client wants to retrieve the resource /index.html using the HTTP/1.1 protocol. The Host header specifies the domain name of the server that the client is requesting the resource from.
Examples of HTTP Requests
Here are some examples of HTTP requests for common web actions:
- Viewing a web page:
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1 Host: example.com - Submitting a form:
POST /login HTTP/1.1 Host: example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded username=johndoe&password=password123 - Uploading a file:
PUT /upload/file.txt HTTP/1.1 Host: example.com Content-Type: text/plain This is the contents of the file. - Deleting a file:
DELETE /upload/file.txt HTTP/1.1 Host: example.com Conclusion
HTTP requests are the foundation of the World Wide Web. They allow clients to retrieve resources from servers, create and update resources, and delete resources. Understanding how HTTP requests work is essential for anyone who wants to develop web applications or understand how the web works.
HTTP Request Methods
HTTP request methods are used to specify the desired action to be performed on a resource. The most common HTTP request methods are:
- GET: This method is used to retrieve a representation of the specified resource.
- POST: This method is used to submit an entity to the specified resource, often causing a change in state or side effects on the server.
- PUT: This method replaces all current representations of the target resource with the request payload.
- DELETE: This method deletes the specified resource.
Other HTTP request methods include:
- OPTIONS: This method describes the communication options for the target resource.
- HEAD: This method asks for a response identical to a GET request, but without the response body.
- PATCH: This method applies partial modifications to a resource.
- TRACE: This method performs a message loop-back test along the path to the target resource.
HTTP Request Headers
HTTP request headers contain additional information about the request, such as the content
WebHTTP requests are messages formatted in the HTTP protocol that are sent from a client to a server that is capable of to responding to them. The messages are. WebHTTP headers. HTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response. An HTTP header consists of its case. WebHTTP - Requests. An HTTP client sends an HTTP request to a server in the form of a request message which includes following format: A Request-line. Zero or more header. WebAn HTTP request is made by a client, to a named host, which islocated on a server. The aim of the request is to access a resource on theserver. To make the. WebWhat is HTTP? The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is designed to enable communications between clients and servers. HTTP works as a request-response. WebAn HTTP request is an action to be performed on a resource identified by a given Request-URL. Request methods are case-sensitive, and should always be noted in upper case..
What Is A Request In Http, Parts of an HTTP Request, 2.11 MB, 01:32, 104,306, Udacity, 2016-06-06T17:45:12.000000Z, 2, HTTP Messages - HTTP | MDN, 538 x 1174, jpg, , 3, what-is-a-request-in-http
What Is A Request In Http.
This video is part of the Udacity course "Designing RESTful APIs". Watch the full course at udacity.com/course/ud388
What Is A Request In Http, WebAn HTTP request is made by a client, to a named host, which islocated on a server. The aim of the request is to access a resource on theserver. To make the. WebWhat is HTTP? The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is designed to enable communications between clients and servers. HTTP works as a request-response. WebAn HTTP request is an action to be performed on a resource identified by a given Request-URL. Request methods are case-sensitive, and should always be noted in upper case..

HTTP Messages - HTTP | MDN - Source: developer.mozilla.org
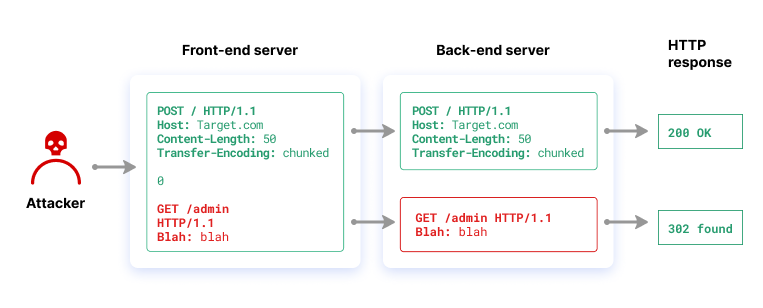
What Is HTTP Request Smuggling? | Attack Examples | Imperva - Source: imperva.com
HTTP Request, HTTP Response, Context and Headers : Part III. | by Rohit Patil | Medium - Source: medium.com
What is options request in http kinsta.com › knowledgebase › what-is-an-http-requestWhat Is an HTTP Request? - Kinsta
What is options request in http HTTP is a protocol. In fact, the acronym stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol. This protocol governs the structure and language of the requests and responses that take place between clients and servers. The clients are usually web browsers, but they can come in many forms, such as search engine robots. What is a request http.
What is a request http
What is a request http What is a post request in http.
What is a post request in http
What is a post request in http What is a get request in http.
.
What is a get request in http
What is a get request in http What is a request body in http.
.
What is a request body in http
What is a request body in http What is a get request in http.
What is a patch request http www.ryadel.com › en › http-request-response-what-howHTTP Request / Response and E-Commerce - Ryadel
What is a patch request http HTTP Request. The HTTP Request is the call that the client/browser makes to the web server. It is composed of the following elements: Method; URL (possibly including a query string) Request Headers; Request Body; Let's now try to understand its meaning, characteristics, and functioning. Method What is request uri in http.
www.freecodecamp.org › news › http-request-methodsHTTP Request Methods – Get vs Put vs Post Explained with Code ...
HTTP Request Examples. Now that we've covered what an HTTP request is, and why we use them, let's make some requests! We're going to be playing with the GitHub Gist API. "Gist is a simple way to share snippets and pastes with others. All Gists are Git repositories, so they are automatically versioned, forkable and usable from Git , What is a patch request http.
.
.
.
developer.mozilla.org › en-US › docsAn overview of HTTP - HTTP | MDN - MDN Web Docs
HTTP is a client-server protocol: requests are sent by one entity, the user-agent (or a proxy on behalf of it). Most of the time the user-agent is a Web browser, but it can be anything, for example, a robot that crawls the Web to populate and maintain a search engine index. Each individual request is sent to a server, which handles it and , .
.
.
What is request uri in http sematext.com › glossary › http-requestsHTTP Requests Defined: What They Are & How They Work - Sematext
What is request uri in http HTTP Request Structure. An HTTP request is made out of three components: request line, headers and message body. Request Line. The request line or start line is sent by the client in order to start the action on the server. It includes the following elements: an HTTP method. the request-target which can be a URI or an URL to either a path or a , What is a request line http.
What is a request line http medium.com › @S3Curiosity › http-requests-andHTTP Requests and Responses: A Beginner's Guide - Medium
What is a request line http An HTTP request is a message sent by a client (usually a web browser) to a web server to request a resource, typically a web page, image, or data. These requests follow a specific structure and , What is bad request in http.
What is bad request in http www.w3schools.com › whatis › whatis_httpWhat is HTTP - W3Schools
What is bad request in http after the page has loaded What is range request in http.
What is range request in http
What is range request in http What is options request in http.

Post a Comment