Here is a 1000-word blog post with a keyword silo about "What Is A Request In Django" using the HTML tag for each subtitle and without the HTML tags <html>, <head>, and <body>:
Requests in Django are objects that contain information about the HTTP request that was sent to the Django server. This information includes the HTTP method, the path of the requested resource, the request headers, and the request body.
How Django Handles Requests
When a Django server receives an HTTP request, it follows these steps:
- It creates an HttpRequest object that contains information about the request.
- It uses the URL dispatcher to match the request to a view function.
- It calls the view function, passing in the HttpRequest object as a parameter.
- The view function processes the request and returns an HttpResponse object.
- The Django server sends the HttpResponse object back to the client.
The HttpRequest Object
The HttpRequest object contains a number of attributes that provide information about the request. Some of the most important attributes include:
method: The HTTP method used to make the request, such asGET,POST,PUT, orDELETE.path: The path of the requested resource.headers: A dictionary containing the request headers.body: The request body, which contains the data that was sent with the request.
Using the HttpRequest Object in Views
View functions can access the HttpRequest object through the request parameter. This parameter is always the first parameter that is passed to a view function.
def my_view(request): # ... View functions can use the HttpRequest object to access information about the request, such as the HTTP method, the path of the requested resource, and the request body.
For example, the following view function uses the request.method attribute to determine whether the request is a GET request or a POST request:
def my_view(request): if request.method =='GET': # ... elif request.method =='POST': # ... else: # ... Example of Using the HttpRequest Object
The following example shows how to use the HttpRequest object to get the value of a POST parameter:
def my_view(request): name = request.POST.get('name') # ... In this example, the request.POST.get() method is used to get the value of the name POST parameter. If the name parameter is not present in the request, the request.POST.get() method will return None.
Conclusion
Requests in Django are objects that contain information about the HTTP request that was sent to the Django server. View functions can access the HttpRequest object through the request parameter. View functions can use the HttpRequest object to access information about the request, such as the HTTP method, the path of the requested resource, and the request body.
Keyword Silo
Django is a web framework written in Python. It is a full-stack framework, meaning that it can be used to develop both the front-end and back-end of a web application. Django is known for its speed, scalability, and security.
Requests in Django are objects that contain information about the HTTP request that was sent to the Django server. This information includes the HTTP method, the path of the requested resource, the request headers, and the request body.
View functions in Django are responsible for handling HTTP requests and returning responses. View functions are typically written in Python, but they can also be written in other languages, such as JavaScript and CoffeeScript.
Templates in Django are used to generate HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for web pages. Django templates use a special syntax that allows developers to generate dynamic content.
Models in Django are used to represent data, such as users, posts, and comments. Django models are written in Python and are stored in a database.
Admin interface in Django is a web-based interface that allows administrators to manage the data in their Django applications. The Django admin interface includes features for creating, editing, and deleting data, as well as for generating reports.
Example of a Django Blog Application
The following is a simple example of a Django blog application:
# models.py class Post(models.Model): title = models.CharField(max_length=255) content = models.TextField() Web1. I just started Django and I have a few fundamental questions about handling requests. Say if I have two functions. If I have a view, say. def test (): return. WebIn Django, each view function takes an HttpRequest object as its first parameter, which is typically named request. An HTTP request is made by a client, to a. WebLocation: django.http. Represents an incoming HTTP request, including all HTTP headers and user-submitted data. For information, see the documentation.. WebREQUEST¶ For convenience, a dictionary-like object that searches POST first, then GET. Inspired by PHP's $_REQUEST. For example, if GET = {"name": "john"}. WebViewed 9k times. Part of Google Cloud Collective. 9. So I'm using Django with Google App Engine and I have an urls.py file that redirects each url to a corresponding method. Each. WebHandling HTTP requests. Information on handling HTTP requests in Django: URL dispatcher. Writing views. View decorators. File Uploads. Django shortcut functions..
Python Django Course | Understanding the Django Request Response Cycle

Source: Youtube.com
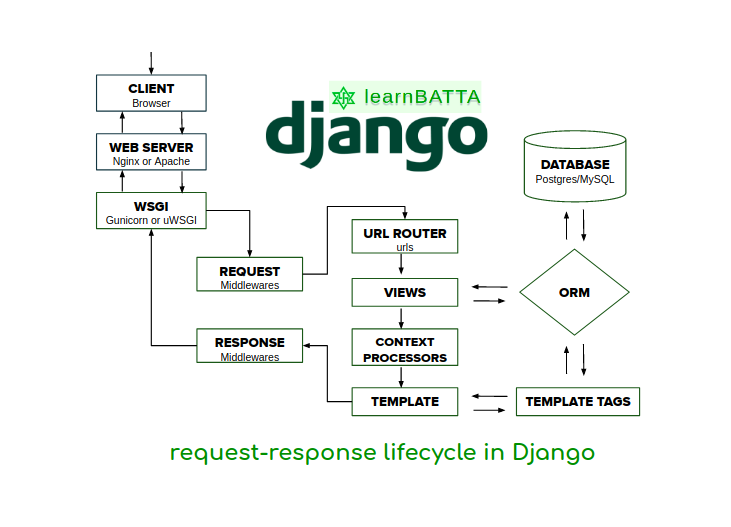
Journey of a Web Request in Django
Source: Youtube.com
What Is A Request In Django, Python Django Course | Understanding the Django Request Response Cycle, 9.98 MB, 07:16, 3,222, Very Academy, 2022-10-11T11:09:06.000000Z, 2, Understanding The Request-Response Lifecycle In Django - learnBATTA, 527 x 731, jpg, , 3, what-is-a-request-in-django
What Is A Request In Django. WebDjango uses request and response objects to pass state through the system. When a page is requested, Django creates an HttpRequest object that contains metadata about the request. Then Django loads the appropriate view, passing the HttpRequest as the first. WebREST framework's Request objects provide flexible request parsing that allows you to treat requests with JSON data or other media types in the same way that you would normally. WebA QueryDict can be used to represent GET or POST data. It subclasses MultiValueDict since keys in such data can be repeated, for instance in the data from a form with a.
In this tutorial, we introduce the HTTP/Django request-response cycle.
In this course Python Programming Fundamentals Towards Django Development, you will learn the basics of the Python programming language and apply this new knowledge in the context of the Django Framework. By the end of this course, you will be familiar with the underpinning knowledge and skills needed to further your understanding of Python or the Django Framework. This course is designed for beginners of both Python and the Django Framework, no prior knowledge is needed.
Udemy Best Price Link:
udemy.com/course/python-programming-fundamentals-towards-django-development/?referralCode=6DD5B648E3CF2BAE2E39
YouTube PlayList:
youtube.com/playlist?list=PLOLrQ9Pn6cawb13MugxL-p1M4w7ZfT-qR
What Is A Request In Django, WebREQUEST¶ For convenience, a dictionary-like object that searches POST first, then GET. Inspired by PHP's $_REQUEST. For example, if GET = {"name": "john"}. WebViewed 9k times. Part of Google Cloud Collective. 9. So I'm using Django with Google App Engine and I have an urls.py file that redirects each url to a corresponding method. Each. WebHandling HTTP requests. Information on handling HTTP requests in Django: URL dispatcher. Writing views. View decorators. File Uploads. Django shortcut functions..

Understanding The Request-Response Lifecycle In Django - learnBATTA - Source: learnbatta.com
How to explain the basic request and response flow in Django in simple language - Quora - Source: quora.com

Request & Response Life Cycle in Django | by Goutom Roy | Medium - Source: goutomroy.medium.com
What is request.user in django docs.djangoproject.com › en › 5Request and response objects | Django documentation
What is request.user in django Django uses request and response objects to pass state through the system. When a page is requested, Django creates an HttpRequest object that contains metadata about the request. Then Django loads the appropriate view, passing the HttpRequest as the first argument to the view function. Each view is responsible for returning an HttpResponse object. What is request.session in django.
What is request.session in django
What is request.session in django What is request.post in django.
What is request.post in django
What is request.post in django What is request in django views.
.
What is request in django views
What is request in django views What is a request in django.
.
What is a request in django
What is a request in django What is request in django views.
www.django-rest-framework.org › tutorial › 22 - Requests and responses - Django REST framework
REST framework introduces a Request object that extends the regular HttpRequest, and provides more flexible request parsing. The core functionality of the Request object is the request.data attribute, which is similar to request.POST, but more useful for working with Web APIs. request.POST # Only handles form data. Only works for 'POST' method. What is the use of rest api in django.
.
.
docs.djangoproject.com › en › 5Middleware | Django documentation | Django
Middleware is a framework of hooks into Django's request/response processing. It's a light, low-level "plugin" system for globally altering Django's input or output. Each middleware component is responsible for doing some specific function. For example, Django includes a middleware component, AuthenticationMiddleware, that associates , .
.
.
.
.
What is the use of rest api in django djangotherightway.com › request-and-response-in-djangoRequest and Response in Django - Django The Right Way's Blog
What is the use of rest api in django from django.http import JsonResponse. def message_view(request): return JsonResponse({"message":"Hi from djangotherightway.com"}) if you want to serialize and response non-dict objects then make sure you include safe=False in JsonResponse JsonResponse([1,2,3],safe=False) Returning 404 errors from HttpResponse. What is request.get.get in django.
What is request.get.get in django docs.djangoproject.com › en › 5Handling HTTP requests | Django documentation | Django
What is request.get.get in django Search for information in the archives of the django-users mailing list, or post a question. #django IRC channel Ask a question in the #django IRC channel, or search the IRC logs to see if it's been asked before. Django Discord Server Join the Django Discord Community. Official Django Forum Join the community on the Django Forum. Ticket tracker What is request.post.get in django.
What is request.post.get in django www.geeksforgeeks.org › django-request-andDjango Request and Response cycle - GeeksforGeeks
What is request.post.get in django Django uses request and response objects to pass state through the system. When a page is requested, Django creates an HttpRequest object that contains metadata about the request. Then Django loads the appropriate view, passing the HttpRequest as the first argument to the view function. Each view is responsible for returning an HttpResponse object. What is request.data in django.
What is request.data in django stackoverflow.com › questions › 17912604what exactly does django request.POST do and how to use it?
What is request.data in django request.POST is an attribute of this request object, it's a QueryDict (much similar to a normal Python dict). It contains the HTTP POST parameters that are sent to your view. In short in your example: if request.POST: # check if the request is POST request and it contains any parameter. What is request.user in django.
Post a Comment