
HTTPS stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure. It is the secure version of HTTP, the protocol used to transfer data between web browsers and websites. HTTPS encrypts all data sent between the browser and the server, protecting it from eavesdropping and tampering.
HTTPS is used by most major websites, including banks, e-commerce sites, and social media platforms. It is also used by many government and educational websites.
How HTTPS Works
HTTPS uses a cryptographic protocol called Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt data. TLS uses public key cryptography, which uses two different keys to encrypt and decrypt data: a public key and a private key.
The public key is known to everyone, while the private key is kept secret by the website owner. When a browser visits a website that uses HTTPS, the browser and the website exchange public keys. The browser then uses the website's public key to encrypt the data it sends to the website. The website then uses its private key to decrypt the data.
TLS also uses digital signatures to ensure that the data has not been tampered with. When the website sends data to the browser, it signs the data with its private key. The browser then verifies the signature using the website's public key. If the signature is valid, the browser knows that the data has not been changed.
Benefits of Using HTTPS
HTTPS offers a number of benefits, including:
- Confidentiality: HTTPS ensures that all data sent between the browser and the server remains confidential. This is important for protecting sensitive information, such as credit card numbers and passwords.
- Integrity: HTTPS ensures that the data sent between the browser and the server has not been tampered with. This is important for preventing fraud and ensuring that users are communicating with the real website.
- Authentication: HTTPS authenticates the website to the browser. This helps to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks, where an attacker intercepts the communication between the browser and the server and poses as the website.
How to Tell if a Website Is Using HTTPS
It is easy to tell if a website is using HTTPS. Just look at the URL in the browser address bar. If the URL starts with https://, then the website is using HTTPS.
You can also look for the lock icon in the browser address bar. If the lock icon is present, then the website is using HTTPS.
Why Is HTTPS Important?
HTTPS is important because it helps to protect users' privacy and security. When users visit a website that uses HTTPS, they can be confident that their data is safe and that they are communicating with the real website.
HTTPS is also important for businesses. Websites that use HTTPS are more likely to be trusted by users, and they are also more likely to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs).
How to Enable HTTPS for Your Website
If you own a website, you should enable HTTPS. This is a relatively simple process, and there are a number of resources available to help you.
Step 1: Get an SSL certificate. An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates your website and encrypts traffic between your website and visitors' browsers. You can get an SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA).
Step 2: Configure your web server. Once you have an SSL certificate, you need to configure your web server to use it. This process will vary depending on the web server you are using.
Step 3: Update your website's URLs. Once you have configured your web server to use HTTPS, you need to update your website's URLs to use https:// instead of http://.
Conclusion
HTTPS is an important security measure for all websites. It helps to protect users' privacy and security, and it is also important for businesses. If you own a website, you should enable HTTPS as soon as possible.
WebIt then opens a connection to the server at that address, using the http protocol as specified. It will initiate a GET request to the server which contains the IP address of. WebHTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response. An HTTP header consists of its case-insensitive name. WebRedirection messages ( 300 – 399) Client error responses ( 400 – 499) Server error responses ( 500 – 599) The status codes listed below are defined by RFC. WebYou can send HTTPS requests from anything able to make HTTPS requests to trigger a Cloud Run-hosted service. Note that all Cloud Run services have a stable. WebThe Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is designed to enable communications between clients and servers. HTTP works as a request-response protocol between a client and.
What Is A Https Request, REST API - Understanding HTTP Request, 4.39 MB, 03:12, 51,361, Tutorialspoint, 2018-05-07T09:19:23.000000Z, 2, What happens when do a HTTPS request in terms of the s part? - Stack Overflow, 346 x 602, jpg, , 3, what-is-a-https-request
What Is A Https Request.
REST API - Understanding HTTP Request
watch more videos at
tutorialspoint.com/videotutorials/index.htm
Lecture By: Mr. Ravikiran S, Tutorials Point India Private Limited
What Is A Https Request, WebRedirection messages ( 300 – 399) Client error responses ( 400 – 499) Server error responses ( 500 – 599) The status codes listed below are defined by RFC. WebYou can send HTTPS requests from anything able to make HTTPS requests to trigger a Cloud Run-hosted service. Note that all Cloud Run services have a stable. WebThe Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is designed to enable communications between clients and servers. HTTP works as a request-response protocol between a client and.

What happens when do a HTTPS request in terms of the s part? - Stack Overflow - Source: stackoverflow.com

Why is HTTP not secure? | HTTP vs. HTTPS | Cloudflare - Source: cloudflare.com
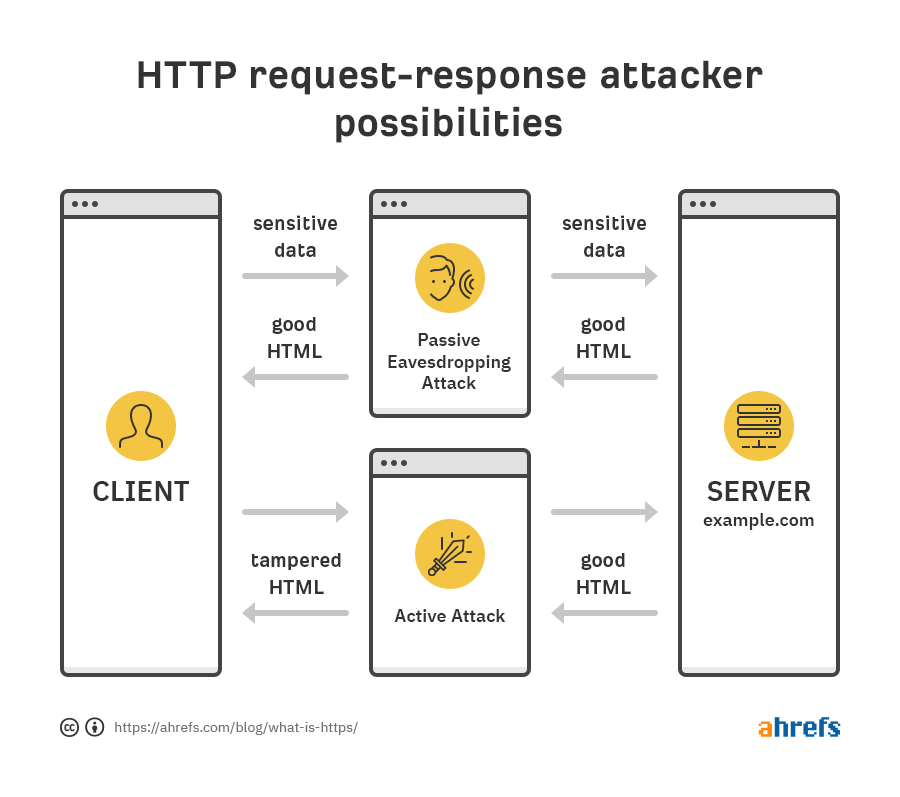
What is HTTPS? Everything You Need to Know - Source: ahrefs.com
What is header in https request
What is header in https request What is https post request.
What is https post request www.cloudflare.com › learning › sslWhat is HTTPS? | Cloudflare
What is https post request Hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS) is the secure version of HTTP, which is the primary protocol used to send data between a web browser and a website. HTTPS is encrypted in order to increase security of data transfer. This is particularly important when users transmit sensitive data, such as by logging into a bank account, email service , What is unverified https request.
What is unverified https request
What is unverified https request What is https request and response.
.
What is https request and response
What is https request and response What is a https request.
.
What is a https request
What is a https request What is https request and response.
www.howtogeek.com › 181767 › htg-explains-what-isWhat Is HTTPS, and Why Should I Care? - How-To Geek
HTTPS is what makes secure online banking and shopping possible. It also provides additional privacy for normal web browsing, too. For example, Google's search engine now defaults to HTTPS connections. This means that people can't see what you're searching for on Google.com. The same goes for Wikipedia and other sites. .
.
.
www.cloudflare.com › learning › sslWhy is HTTP not secure? | HTTP vs. HTTPS | Cloudflare
In HTTPS, how does TLS/SSL encrypt HTTP requests and responses? TLS uses a technology called public key cryptography : there are two keys , a public key and a private key, and the public key is shared with client devices via the server's SSL certificate. .
.
.
.
.
proprivacy.com › guides › https-explainedWhat is HTTPS? - What You Need to Know - ProPrivacy
The name Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) basically denotes standard unsecured (it is the application protocol that allows web pages to connect to each other via hyperlinks). HTTPS web pages are secured using TLS encryption, with the and authentication algorithms determined by the web server. .
www.upguard.com › blog › what-is-httpsWhat is HTTPS? How it Works and Why It's So Important
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is a secured version of HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol). HTTP is a protocol used to transfer data across the Web via a client-server (web browser-web server) model. HTTPS encrypts all data that passes between the browser and server using an encryption protocol called Transport Layer Security (TLS , Difference between http and https request.
Difference between http and https request www.freecodecamp.org › news › what-is-https-http-vsWhat is HTTPS? HTTP vs HTTPS Meaning and How it Works
Difference between http and https request Specifically, HTTP is an application layer protocol and is the primary protocol used for communication and data transfer between a web client and a web server. In a nutshell, HTTP is a set of rules and standards for how hypertext files and all kinds of information are transfered over the web. It's how browsers and servers communicate. What is http and https request.
What is http and https request en.wikipedia.org › wiki › HTTPSHTTPS - Wikipedia
What is http and https request HTTPS encrypts all message contents, including the HTTP headers and the request/response data. With the exception of the possible CCA cryptographic attack described in the limitations section below, an attacker should at most be able to discover that a connection is taking place between two parties, along with their domain names and IP addresses. What is header in https request.


Post a Comment