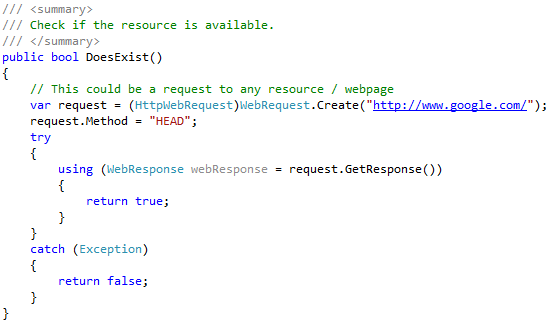
A HEAD request is an HTTP request method that is identical to a GET request, except that the server does not return a message body in the response. This is useful for retrieving meta-information about a resource without having to transfer the entire content.
When to use a HEAD request
HEAD requests can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Checking the availability of a resource
- Checking the size of a resource
- Checking the last modification date of a resource
- Checking the content type of a resource
- Checking the caching headers for a resource
Examples of HEAD requests
Here are some examples of HEAD requests:
HEAD /index.html HEAD /images/my-image.png HEAD /videos/my-video.mp4 Benefits of using HEAD requests
There are several benefits to using HEAD requests:
- HEAD requests are faster than GET requests because the server does not have to transfer the entire content of the resource.
- HEAD requests can be used to conserve bandwidth.
- HEAD requests can be used to avoid downloading resources that are not needed.
How to send a HEAD request
HEAD requests can be sent using any HTTP client. For example, to send a HEAD request using curl, you can use the following command:
curl -I https://www.example.com/index.html Example response to a HEAD request
The following is an example of a response to a HEAD request:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 1234 Last-Modified: Tue, 12 Oct 2023 15:46:56 GMT The response headers contain information about the resource, such as the content type, content length, and last modification date.
Use cases for HEAD requests
Here are some use cases for HEAD requests:
- Checking for broken links: HEAD requests can be used to check for broken links on a website. To do this, you can send a HEAD request to each link on the website. If the server returns a 200 OK status code, then the link is working. If the server returns a 404 Not Found status code, then the link is broken.
- Pre-caching resources: HEAD requests can be used to pre-cache resources before they are needed. This can improve the performance of web applications. For example, a web application could send a HEAD request to a CSS file before the file is needed to render a page. This will ensure that the CSS file is already cached when the user visits the page.
- Checking for updates: HEAD requests can be used to check if a resource has been updated. To do this, you can store the Last-Modified header from a previous HEAD request. The next time you need the resource, you can send a HEAD request and compare the Last-Modified header to the stored header. If the Last-Modified header has changed, then the resource has been updated.
Conclusion
HEAD requests are a powerful tool that can be used to retrieve meta-information about resources without having to transfer the entire content. HEAD requests can be used for a variety of purposes, such as checking for broken links, pre-caching resources, and checking for updates.
Keyword silo
The keyword silo for this blog post is:
- Head request
- HTTP method
- Meta-information
- Resource
- GET request
- Response body
- Availability
- Size
- Last modification date
- Content type
- Caching headers
- Benefits
- Use cases
HTML format and HTML tags
The following is the HTML format and HTML tags for the blog post:
A HEAD request is an HTTP request method that is identical to a GET request, except that the server does not return a message body in the response. This is useful for retrieving meta-information about a resource without having to transfer the entire content. ## When to use a HEAD request HEAD requests can be used for a variety of purposes, including: * Checking the availability of a resource * Checking the size of a resource * Checking the last modification date of a resource * Checking the content type of a resource * Checking the caching headers for a resource ## Examples of HEAD requests Here are some examples of HEAD requests: HEAD /index.html
HEAD /images/my-image.png
HEAD /videos/my-video.mp4
Benefits of using HEAD requests
There are several benefits to using HEAD requests:
- HEAD requests are faster than GET requests because the server does not have to transfer the entire content of
WebThe http spec says about the HEAD request: The HEAD method is identical to GET except that the server MUST NOT return a message-body in the response. The. WebThe head() method sends a HEAD request to the specified url. HEAD requests are done when you do not need the content of the file, but only the status_code or HTTP headers. WebHTTP Head. The HEAD request is similar to a GET request. Instead of returning the resource, it only returns the headers associated with the resource. A. WebThe HTTP HEAD requests, like an HTTP GET, cannot contain data in the message's body; the request data must be passed to the server in the URL. In this HTTP. WebLast updated by: fscholz , Jun 7, 2017, 9:48:56 AM. The HTTP HEAD method requests the headers that are returned if the specified resource would be. WebThe HEAD Method. HEAD is almost identical to GET, but without the response body. In other words, if GET /users returns a list of users, then HEAD /users will make the.
What is the Head Method | HTTP and REST API Interview Q&A | Under 60 Seconds

Source: Youtube.com
REST API Series | Tutorial 7: HTTP Methods - GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD, OPTIONS, PATCH

Source: Youtube.com
What Is A Head Request, What is the Head Method | HTTP and REST API Interview Q&A | Under 60 Seconds, 726.56 kB, 00:31, 973, Joshua Cadavez, 2020-07-21T19:00:10.000000Z, 2, HTTP HEAD Request - Benefits / Usages, 324 x 550, jpg, , 3, what-is-a-head-request
What Is A Head Request. WebThe HEAD method is identical to GET except that the server MUST NOT return a message-body in the response. The metainformation contained in the HTTP headers in response.
Like and Subscribe if you enjoy my content!
Sources:
w3schools.com/tags/ref_httpmethods.asp
*******************************************************************************************
Follow me on:
Twitter - twitter.com/JoshuaCadavez
LinkedIn - linkedin.com/in/joshuacadavez
GitHub - github.com/JoshuaTheEngineer
What Is A Head Request, WebThe HTTP HEAD requests, like an HTTP GET, cannot contain data in the message's body; the request data must be passed to the server in the URL. In this HTTP. WebLast updated by: fscholz , Jun 7, 2017, 9:48:56 AM. The HTTP HEAD method requests the headers that are returned if the specified resource would be. WebThe HEAD Method. HEAD is almost identical to GET, but without the response body. In other words, if GET /users returns a list of users, then HEAD /users will make the.

HTTP HEAD Request - Benefits / Usages - Source: deanhume.com

HEAD method - Python requests - GeeksforGeeks - Source: geeksforgeeks.org
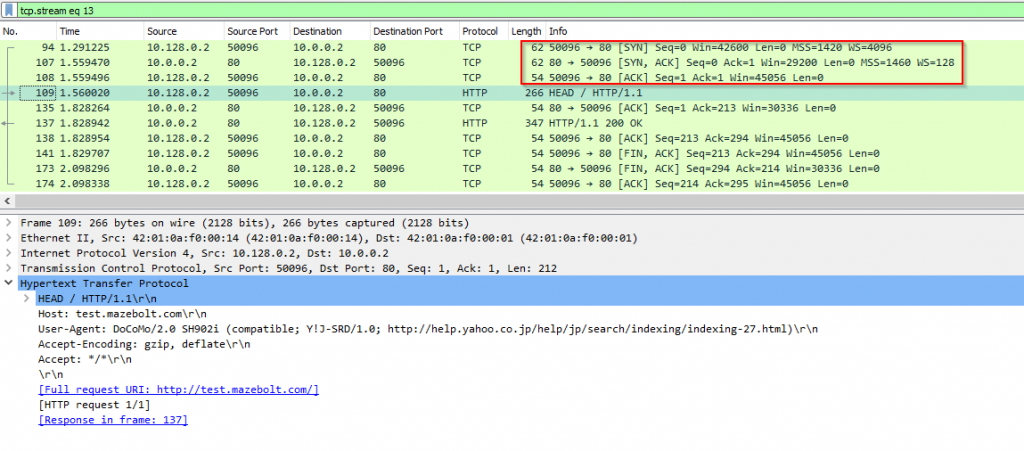
HTTP HEAD Flood | MazeBolt Knowledge Base | MazeBolt Knowledge Base - Source: kb.mazebolt.com
What is a head call in the marines
What is a head call in the marines What is head request used for.
What is head request used for
What is head request used for What is head request in rest api.
What is head request in rest api
What is head request in rest api What is a head request curl.
.
What is a head request curl
What is a head request curl What is a head request.
.
What is a head request
What is a head request What is a head request curl.
www.jsdelivr.com › blog › what-are-http-get-and-headWhat Are HTTP GET and HEAD Requests and How to Leverage Their ...
In conclusion, HTTP GET, and HEAD requests are fundamental components of web development and troubleshooting. GET requests to retrieve data from web servers, making them essential for browsing the web and integrating with APIs. On the other hand, HEAD requests provide valuable information about resources without transferring unnecessary data. .
testerops.com › 2023/05/03 › what-is-a-head-requestWhat is a HEAD request really? – TESTEROPS
HEAD REQUEST. The HEAD request method is similar to the GET method, but it only returns the header information of a resource. As per the MDN definition –. The HTTP HEAD method requests the headers that would be returned if the HEAD request's URL was instead requested with the HTTP GET method. The server will not return the body of the , .
.
.
.
www.telerik.com › blogs › understanding-head-httpUnderstanding HEAD, HTTP/204 and HTTP/206 - Telerik
The HEAD Request Method. The first request returned a HTTP/200, but you'll notice that the server didn't send any bytes in the body. If you examine the headers using the Inspectors tab, you will notice that the client used the HEAD request method. The HEAD method allows the client to query the server for the headers for a given resource , .
.
.
apidog.com › blog › http-head-methodWhat is HTTP HEAD Method? - apidog.com
The HTTP HEAD method is a request method used to retrieve metadata about a resource without actually downloading its content. It is similar to the HTTP GET method in that it requests information from a server, but the server does not return a message-body in response to a HEAD request, whereas a GET request returns the message-body in addition , .
stackoverflow.com › questions › 16539269http HEAD vs GET performance - Stack Overflow
It also depends on the approach you use server-side. It usually may take the same server time to process a GET request or a HEAD request, because the server might need to know the final body to calculate the Content-Length header value, which is an important information in a response of a HEAD request. Unless there is some other more optimized , Head request type.
Head request type reqbin.com › Article › HttpHeadWhat is HTTP HEAD Request Method? - ReqBin
Head request type The HTTP HEAD request is used to check the availability, size, and last modification date of a resource without downloading it (as indicated by the Content-Length and Last-Modified headers). For example, we can send a GET request to check if a PDF file is available for download. The server will return a 200 status code if the file is available , What is a head call.
What is a head call developer.mozilla.org › docs › WebHEAD - HTTP | MDN - MDN Web Docs
What is a head call The HTTP HEAD method requests the headers that would be returned if the HEAD request's URL was instead requested with the HTTP GET method. For example, if a URL might produce a large download, a HEAD request could read its Content-Length header to check the filesize without actually downloading the file. What is a head call in the marines.
Post a Comment