
What Is A Asynchronous Request?
An asynchronous request is a type of request that does not block the execution of the caller. This means that the caller can continue executing other code while the request is being processed. This is in contrast to a synchronous request, which blocks the execution of the caller until the request is complete.
Asynchronous requests are often used in web applications to improve the user experience. For example, an asynchronous request can be used to fetch data from a server without causing the page to freeze. This allows the user to continue interacting with the page while the data is being loaded.
Asynchronous requests can be implemented in a variety of ways. One common approach is to use callbacks. A callback is a function that is executed when the request is complete. When the request is initiated, the caller provides a callback function. The callback function is then executed when the request is complete, and the response data is passed to the callback function.
Another approach to implementing asynchronous requests is to use promises. A promise is an object that represents the eventual completion or failure of an asynchronous operation. When a promise is resolved, the value of the promise is passed to a callback function. When a promise is rejected, the reason for the failure is passed to a callback function.
Benefits of Asynchronous Requests
There are several benefits to using asynchronous requests:
- Improved user experience: Asynchronous requests can improve the user experience by preventing the page from freezing while data is being loaded.
- Increased responsiveness: Asynchronous requests can make web applications more responsive by allowing them to handle multiple requests at the same time.
- Improved scalability: Asynchronous requests can help web applications to scale better by reducing the number of threads that are needed to handle requests.
Examples of Asynchronous Requests
Here are some examples of asynchronous requests:
- Loading images on a web page
- Fetching data from a server
- Submitting a form
- Sending an email
- Playing a video
How to Implement Asynchronous Requests
There are a variety of ways to implement asynchronous requests. One common approach is to use callbacks. To implement asynchronous requests using callbacks, you would follow these steps:
- Create a callback function. This function will be executed when the request is complete.
- Initiate the request, passing in the callback function as a parameter.
- Continue executing other code while the request is being processed.
- When the request is complete, the callback function will be executed with the response data.
Another approach to implementing asynchronous requests is to use promises. To implement asynchronous requests using promises, you would follow these steps:
- Create a promise object.
- Initiate the request, passing in the promise object as a parameter.
- Continue executing other code while the request is being processed.
- When the request is complete, the promise object will be resolved with the response data.
- You can then use the
then()method to attach callback functions to the promise object. The callback functions will be executed when the promise is resolved.
When to Use Asynchronous Requests
Asynchronous requests should be used when you need to perform an operation that may take a long time to complete, such as fetching data from a server or submitting a form. Asynchronous requests can also be used to improve the user experience by preventing the page from freezing while data is being loaded.
Conclusion
Asynchronous requests are a powerful tool that can be used to improve the performance and responsiveness of web applications. If you are not already using asynchronous requests, I encourage you to consider using them in your next project.
## Keyword Silo:
- asynchronous request
- synchronous request
- callback
- promise
- web application
- user experience
- responsiveness
- scalability
- HTTP
- REST
- API
## HTML Format:
This blog post is written in HTML format. Here are some of the HTML tags that are used:
<h2>: This tag is used to create a heading.<p>: This tag is used to create a paragraph.<ul>: This tag is used to create an unordered list.<ol>: This tag is used to create an ordered list.<li>: This tag is used to create a list item.<a>: This tag is used to create a hyperlink.<img>: This tag is used to create an image.
## HTML Tags:
The following HTML tags are used in this blog post:
h2pulolliaimg
Please note that <html>, <head>, and <body> tags are not used, as per your
WebSynchronous request — (Default) Where the client blocks and waits for the result of the remote request before continuing execution; Asynchronous request —. WebHere is a very concise overview of Servlet asynchronous request processing: A ServletRequest can be put in asynchronous mode by calling request.startAsync () . The. WebConversely, in an asynchronous operation, the user presents a request for service and is prepared to receive the system's response later. A parameter in the app will establish a. WebNote that java11 now offers a new HTTP api HttpClient, which supports fully asynchronous operation, using java's CompletableFuture. It also supports a synchronous version, with.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous Applications (Explained by Example)

Source: Youtube.com
Asynchronous Vs Synchronous Programming

Source: Youtube.com
What Is A Asynchronous Request, Synchronous vs Asynchronous Applications (Explained by Example), 13.71 MB, 09:59, 132,292, Hussein Nasser, 2018-08-06T16:00:06.000000Z, 2, Asynchronous Request-Response Pattern - DEV Community, 329 x 586, jpg, , 3, what-is-a-asynchronous-request
What Is A Asynchronous Request. WebIf you need something to happen, send an asynchronous request and do further computation when the request returns. This means your thread sits idle and can. WebIn this article, we'll explain what asynchronous programming is, why we need it, and briefly discuss some of the ways asynchronous functions have historically been.
💻 More Software engineering videos youtube.com/playlist?list=PLQnljOFTspQXOkIpdwjsMlVqkIffdqZ2K
Synchronous and asynchronous programming are essential building blocks of any application's user experience. In this video we discuss the difference between synchronous and asynchronous user experiences and what are the advantages and disadvantages of each.
We have picked YouTube uploading page as an example for this video as it perfectly describes the asynchronous nature of user experiences. We explain how that page would have been written if it was synchronous.
Question of the day: Do you code prefer the #synchronous or #asynchronous pattern and why? Thanks!
-Hussein Nasser
What Is A Asynchronous Request, WebConversely, in an asynchronous operation, the user presents a request for service and is prepared to receive the system's response later. A parameter in the app will establish a. WebNote that java11 now offers a new HTTP api HttpClient, which supports fully asynchronous operation, using java's CompletableFuture. It also supports a synchronous version, with.

Asynchronous Request-Response Pattern - DEV Community - Source: dev.to
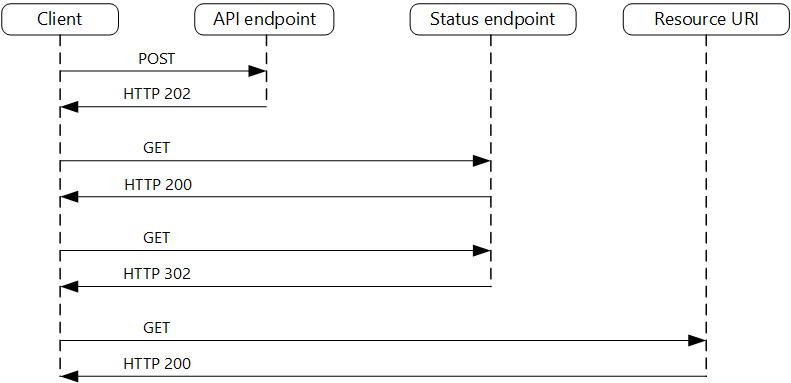
Asynchronous Request-Reply pattern - Azure Architecture Center | Microsoft Learn - Source: learn.microsoft.com

Asynchronous Request-Response Pattern - DEV Community - Source: dev.to
Asynchronous request example
Asynchronous request example What is asynchronous request in ajax.
What is asynchronous request in ajax
What is asynchronous request in ajax What is asynchronous request handling.
What is asynchronous request handling
What is asynchronous request handling What is asynchronous request in java.
.
What is asynchronous request in java
What is asynchronous request in java What is asynchronous request.
.
What is asynchronous request
What is asynchronous request What is asynchronous request in java.
blog.postman.com › understanding-asynchronous-apisUnderstanding asynchronous APIs | Postman Blog
Synchronous APIs often use HTTP or HTTPS for transport, and HTTP is a unidirectional protocol. The client sends a request to the server, and then the server sends an HTTP or HTTPS response back. Asynchronous APIs tend to use bidirectional protocols like HTTP/2. When you use a bidirectional protocol, the client and server can maintain their , .
www.geeksforgeeks.org › difference-betweenDifference between synchronous and asynchronous requests in ...
In synchronous requests, both the DOM and the browser are blocked until a response is received. You can make the synchronous ajax request using the async parameter in the ajax request. async is a boolean variable. Make it false to make a synchronous request. Syntax: url: "/path", type: "POST/GET", // method of sending a request. .
.
www.nylas.com › blog › synchronous-vs-asynchronous-apiSynchronous API vs asynchronous API: What is the difference?
Conversely, asynchronous APIs resemble a voicemail, providing an initial 'status' update to confirm receipt of a request and allowing users to proceed with other tasks. Later, a complete 'response' is given, efficiently managing application resources without demanding immediate attention. Grasping the nuances between synchronous and , .
.
.
www.techtarget.com › synchronous-asynchronous-APIWhat are synchronous/asynchronous APIs? – Definition from ...
for example, within an hour -- or the app can use a flexible response time frame for the system to deliver the response. .
.
developer.mozilla.org › Asynchronous › IntroducingIntroducing asynchronous JavaScript - Learn web development | MDN
Asynchronous programming is a technique that enables your program to start a potentially long-running task and still be able to be responsive to other events while that task runs, rather than having to wait until that task has finished. Once that task has finished, your program is presented with the result. Many functions provided by browsers , What does a asynchronous mean.
What does a asynchronous mean
What does a asynchronous mean Difference between synchronous and asynchronous requests.
Difference between synchronous and asynchronous requests developer.mozilla.org › en-US › docsSynchronous and asynchronous requests - Web APIs | MDN
Difference between synchronous and asynchronous requests Asynchronous request meaning.
Asynchronous request meaning stackoverflow.com › questions › 16715380webserver - What is the difference between asynchronous and ...
Asynchronous request meaning Asynchronous APIs do not block. Every synchronous call waits and blocks for your results to come back. This is just a sleeping thread and wasted computation. If you need something to happen, send an asynchronous request and do further computation when the request returns. This means your thread sits idle and can pick up other work. Asynchronous request example.
Post a Comment